Comparison of scientific literature review timelines: manual method vs. the NOÉ application
24 nov. 2025
5 min read
Study
The study evaluates the time savings provided by NOÉ, an AI application dedicated to healthcare literature reviews, compared with a traditional manual method for the clinical evaluation of medical devices.
Study objective
In the medical device field, systematic literature review is an essential step to establish the state of the art and document clinical evaluation. However, this task remains time-consuming, requiring significant time and human resources. It is within this context that we tested NOÉ, our web-based artificial intelligence application dedicated to healthcare literature reviews.
Objective: to concretely measure time savings compared with a traditional manual method (Excel).
This study aims to objectively assess the time savings delivered by NOÉ compared with the conventional manual method for scientific literature reviews conducted as part of medical device clinical evaluation.
Methodology

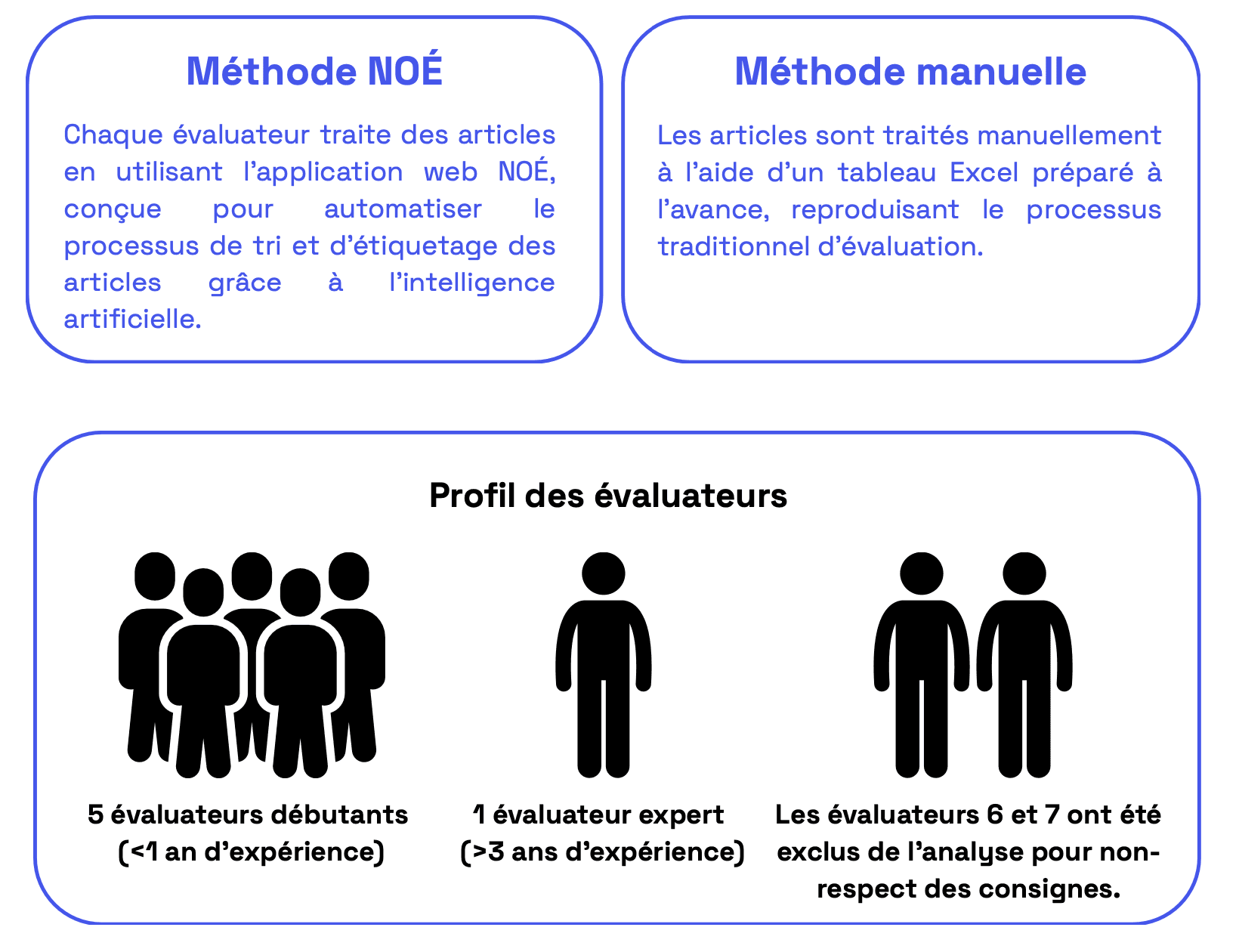
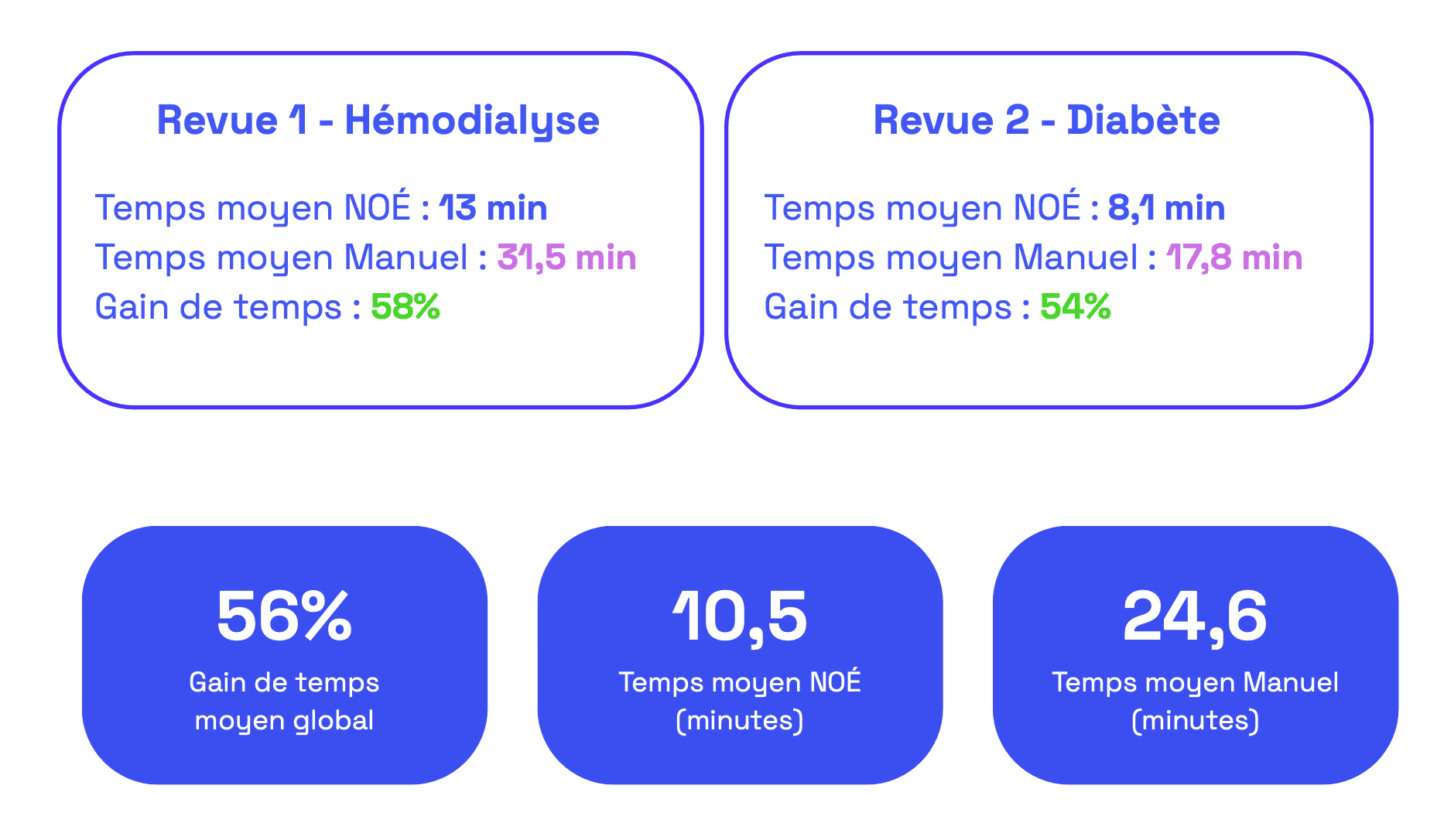
Detailed results
Processing time per reviewer
Évaluateur | Revue #1 NOÉ (min) | Revue #1 Manuelle (min) | Temps gagné (min) | Revue #2 NOÉ (min) | Revue #2 Manuelle (min) | Temps gagné (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Évaluateur 1 | 12 | 30 | 18 | 7,5 | 15 | 7,5 |
Évaluateur 2 | 19 | 50 | 31 | 9 | 20 | 11 |
Évaluateur 4 | 15 | 32 | 17 | 10 | 21 | 11 |
Évaluateur 10 | 6 | 14 | 8 | 6 | 15 | 9 |
Comparative analysis by review
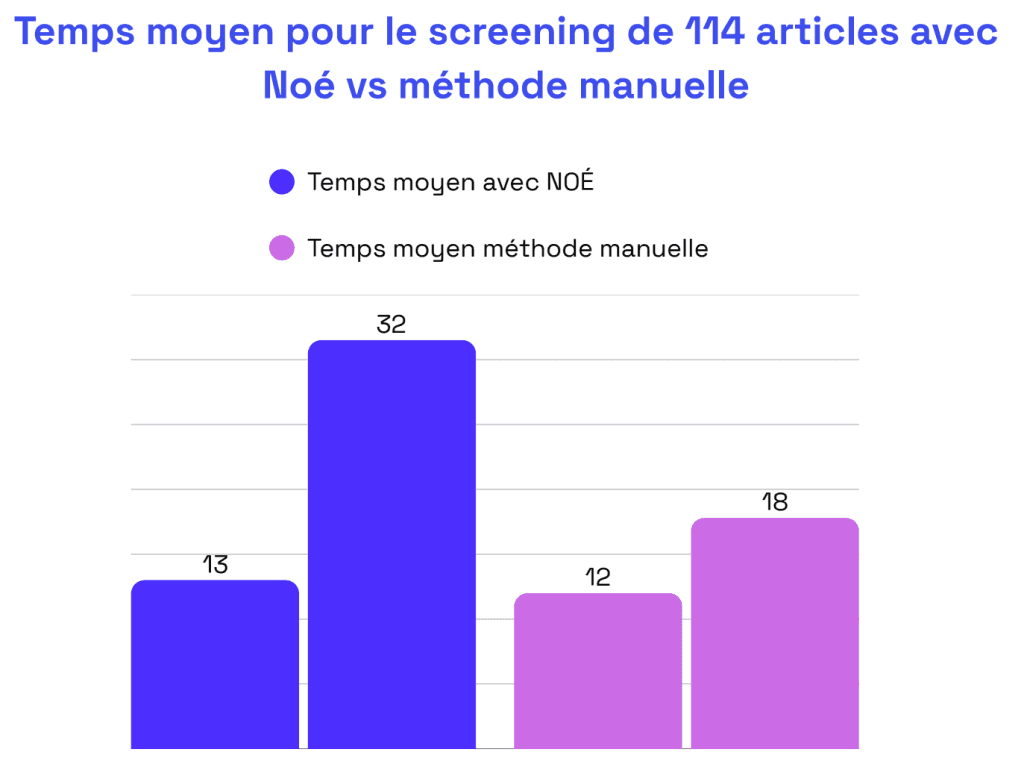
Results analysis
The quantitative analysis of the study shows that the NOÉ web application enables a significant reduction in the time required for the screening phase of the literature review, compared with an optimized manual method using Excel.
The observed time savings, exceeding 50% in all valid cases, confirm the potential of AI-based tools to transform and optimize literature research processes in the biomedical sector.
This increased efficiency allows teams to focus on higher value-added tasks, thereby accelerating the overall clinical evaluation process for medical devices.
Conclusion
NOÉ demonstrates significant potential to improve the efficiency of scientific literature reviews, with observed time savings of up to 62%, and an average of 56% across all reviews.
From the very first review, users saved time with NOÉ. The second review confirmed the stability of these performances, with consistent gains after an initial exposure to the tool. This suggests that NOÉ provides immediate and sustainable time savings.
How does NOÉ help save time?
Intelligent automation
NOÉ’s machine learning algorithms automatically analyze articles and propose a pre-screening based on the defined eligibility criteria.
Natural language processing
NOÉ uses NLP techniques specialized for the biomedical domain, enabling more precise analysis of scientific content.
Optimized interface
NOÉ’s web interface is designed to minimize clicks and optimize the review workflow, reducing the cognitive load on reviewers.
